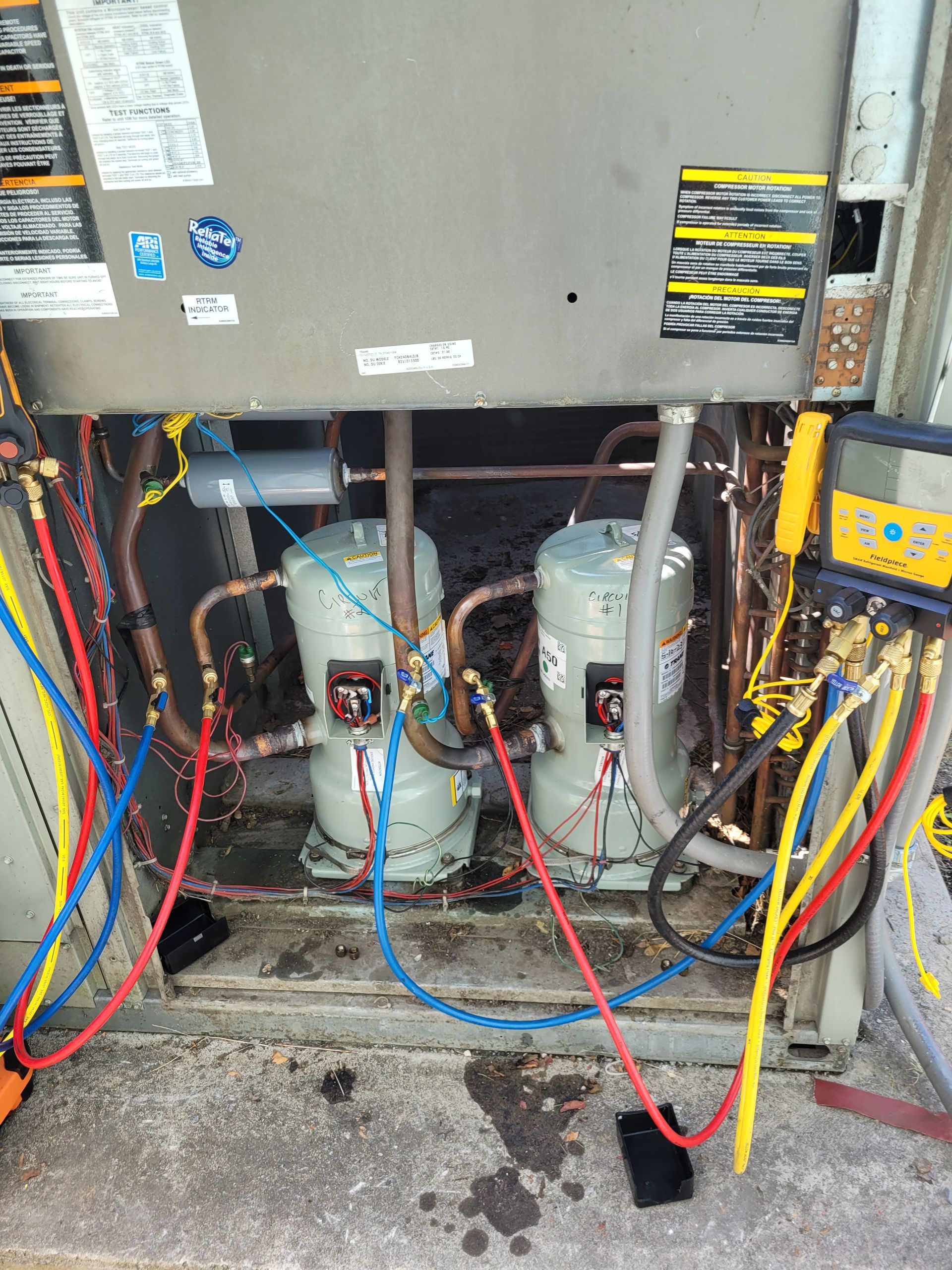
Commercial Compressor Repair Charlottesville
Industrial Compressor Replacement Harrisonburg VA
HVAC and Refrigeration Compressor Repair and Replacement in Charlottesville and Harrisonburg VA should be provided by experienced, competent and commercial licensed technicians only. In the realm of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), and refrigeration systems, compressors play a pivotal role. They are responsible for circulating refrigerant, which absorbs and releases heat, thus regulating temperature. When a commercial compressor malfunctions, it can halt an entire system’s operation, leading to uncomfortable indoor climates or spoilage of refrigerated goods. This article delves into the technicalities of compressor repair and replacement, offering insights into diagnosis, processes, tools, and decision-making.
THE FREON CYCLE | THE REFRIGERANT LOOP
Their primary function of the Compressor in a HVAC or Refrigeration system is to compress or condense the refrigerant into its liquid form, increasing its pressure. Then the liquid freon refrigerant leaves the compressor, it flows through the system where it takes on the heat and ambient temperature of the evaporator (inside the freezer or refrigerator or the evaporator coil in the air handler that heats or cools your living or working environment), which makes the freon boil and expand into a gas. Then the gaseous freon returns to the compressor where it is again condensed into a liquid and is relieved of the heat that was absorbed in the evaporator. This is known as the freon cycle or refrigerant loop.
UNDERSTANDING HVAC AND REFRIGERATION COMPRESSORS
The choice of type of compressor depends on factors including:
- system size
- temperature set point
- efficiency needs, and
- cost.
Common types of compressors include:
1. RECIPROCATING COMPRESSORS
Use pistons for compression.
2. SCROLL COMPRESSORS
Utilize interlocking scrolls for efficient operation.
3.
ROTARY COMPRESSORS
Employ rotating mechanisms and are common in residential units.
4.
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
Are used in large commercial systems.
5.
SCREW COMPRESSORS
Are designed for industrial applications.

SIGNS OF COMPRESSOR FAILURE
Compressors wear down over time due to heavy usage or poor maintenance.
Signs of Compressor failure include:
1. SYSTEM NOT COOLING/HEATING PROPERLY
Reduced efficiency is often the first indicator.
2.
UNUSUAL NOISES
Clicking, clanking, or hissing noises could indicate mechanical issues.
3.
CIRCUIT BREAKER TRIPS
A struggling compressor may draw excessive power.
4.
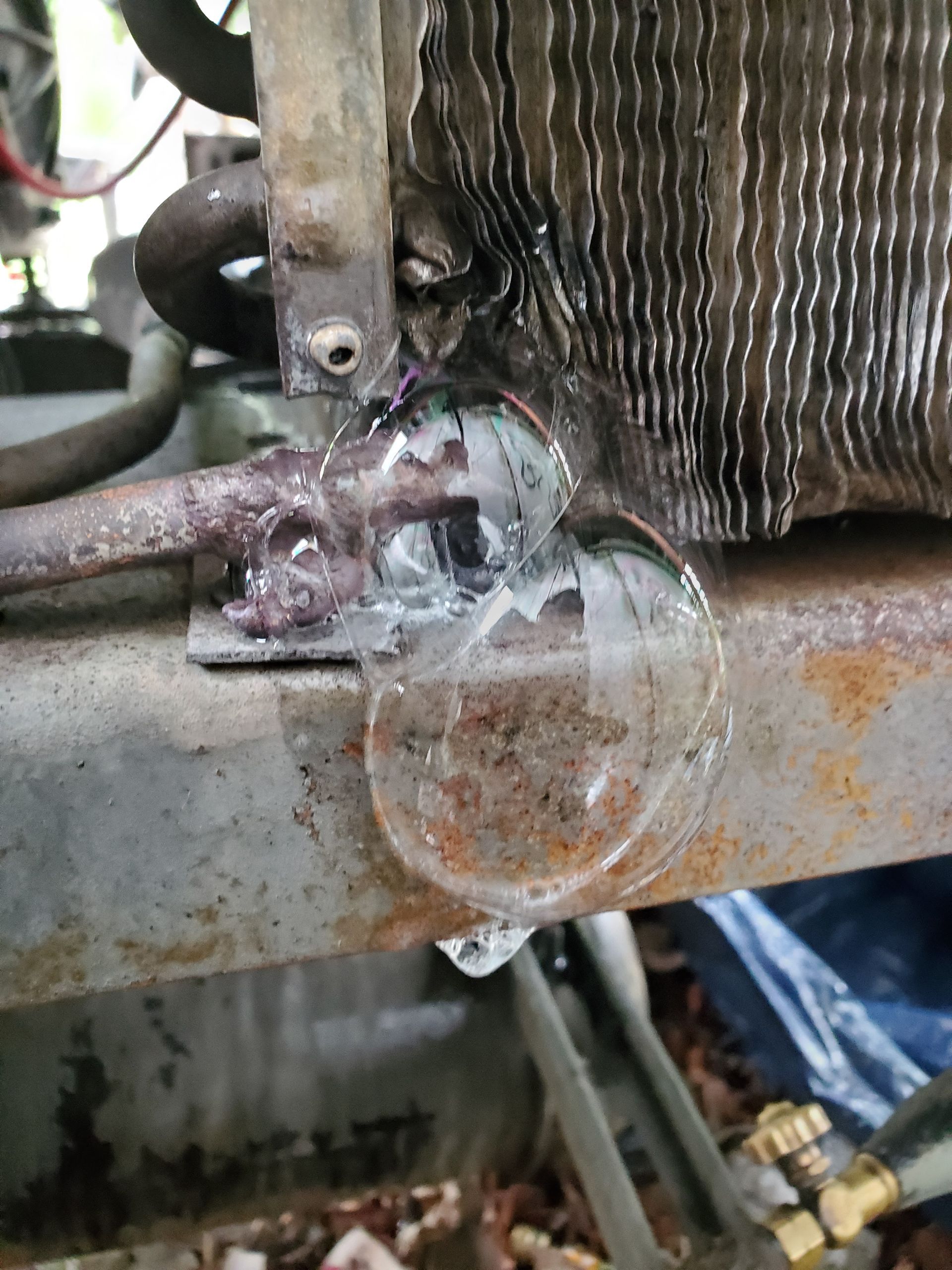
REFRIGERANT LEAKS
Visible leaks may point to internal damage.
5.
BURNT SMELL
Could signify electrical issues.
6. UNUSUALLY HIGH SUCTION LINE PRESSURES
Signifies severe internal compressor damage.
7. ELECTRICAL USAGE BY THE COMPRESSOR
that is more than 20% above or below its FLA (Full Load Amps), means the compressor is worn out beyond repair.
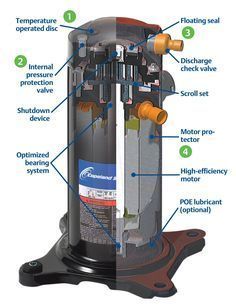
EARLY IDENTIFICATION OF COMPRESSOR FAILURE CAN REDUCE REPAIR COSTS AND PREVENT TOTAL SYSTEM SHUTDOWNS.
1.
DIAGNOSING COMPRESSOR ISSUES:
Proper diagnosis, which is crucial before attempting any compressor repair or replacement, should be performed by a licensed, experienced technician.
Key steps include:
2.
INSPECTING ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
Loose or corroded connections can lead to poor performance and cause severe compressor damage.
3.
TESTING CAPACITORS AND RELAYS
Faulty electrical components often mimic compressor failure, and will fool the inexperienced technician or DIYr.
3.
MEASURING REFRIGERANT LEVELS
Improper levels can overwork the compressor.
4.
EVALUATING COMPRESSOR WINDINGS
Using an ohmmeter, technicians can identify electrical faults.
5.
CHECKING FOR BLOCKAGES
Debris in the refrigerant line may hinder operation, reduce efficiency and overwork the compressor.
Having the right diagnostic tools—such as multi-meters, gauges—is essential.
COMPRESSOR REPAIR SOLUTIONS
However, COMPRESSOR REPAIR is only viable if the damage is limited and the compressor has not reached the end of its service life.
1.
COMPRESSOR REPAIR WHEN IS IT AN OPTION? Not all compressor issues demand replacement; some can be repaired effectively.
2.
REFRIGERANT RECHARGE
If refrigerant levels are low due to minor leaks, finding and properly fixing the leak, then correctly recharging the freon may suffice.
3.
REPLACING ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
Swapping out faulty capacitors, contactors, or relays can restore functionality.
4.
FIXING VALVE OR SEAL ISSUES
Minor repairs can stop freon leaks and extend a compressor’s life.

COMPRESSOR REPLACEMENT: MAKING THE DECISION
If a compressor repair isn’t feasible, replacement becomes necessary. Consider the following factors:
1. THE SYSTEM'S AGE
Compressors older than 10-15 years may not be worth repairing.
2. COST OF REPAIR vs. REPLACEMENT
If repair costs exceed 40% of the replacement cost, opting for a new compressor is wise.
3.
EFFICIENCY STANDARDS
Modern compressors are more energy-efficient, reducing long-term costs.
4.
WARRANTY STATUS
Some manufacturers offer warranties that cover replacements. We will file all warranty paperwork for you.
STEPS IN COMPRESSOR REPLACEMENT
Replacing a compressor is a technical process best performed by certified, experienced professionals. Using quality replacement parts and adhering to manufacturer guidelines is paramount.
Here’s a general overview:
1.
REFRIGERANT RECOVERY
Safely removing the refrigerant is a regulatory requirement.
2.
DISCONNECTING THE OLD COMPRESSOR
Involves properly detaching electrical connections and refrigerant lines.
3.
INSTALLING THE NEW COMPRESSOR
Proper alignment and secure fittings are critical.
4.
Recharging the System
With virgin freon only because the old refrigerant may never be reused if it was taken from your system after the old compressor failed and had been replaced.
5.
Pressure Testing and Calibration
Ensures the new compressor operates correctly.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
A well-maintained system not only performs more efficiently, it operates longer and requires less repairs. To prolong the life of compressors, regular preventive maintenance is extremely important:
1.
CLEANING COILS
Dirty coils can strain the compressor.
2.
CHECKING REFRIGERANT LEVELS
Ensures optimal operation. Over-filling or under-filling freon will damage the compressor.
3.
PROPERLY LUBRICATING MOVING PARTS
Reduces wear and tear.
4. INSPECTION OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENT, WIRING & CONNECTIONS BOTH VISUALLY & WITH THE PROPER GAUGES & METERS
Prevents unexpected failures.
Scheduling Annual Tune-Ups: Professional inspections can identify issues early.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONSIDERATIONS | 608 Certification
The disposal of old compressors and refrigerants must be done responsibly by certified technicians. CFCs and HCFCs, commonly found in older refrigerants, contribute to ozone depletion. Compliance with regulations like the Clean Air Act (AKA 608 Certification) ensures the technician understands safe handling of freon. Additionally, upgrading to compressors compatible with eco-friendly refrigerants can greatly reduce environmental impact.
EXPERT COMPRESSOR SERVICE AND REPAIRS
CHARLOTTESVILLE
HVAC and Refrigeration Compressors are integral to modern comfort and food preservation. Understanding how to diagnose, repair, and replace them can save time, money, and energy and; therefore, should only be performed by licensed and experienced technicians in Charlottesville or Harrisonburg VA. Whether it’s a minor fix or a complete replacement, always prioritize professional expertise and adherence to safety standards. Regular maintenance and attention to environmental sustainability can ensure these systems operate efficiently for many years to come.